 What is NixOS?
What is NixOS?
NixOS is a Linux distribution with a unique approach to package and configuration management. Built on top of the Nix package manager, it is completely declarative, makes upgrading systems reliable, and has many other advantages.
I think NixOS is a very interesting and useful Linux system, but a bit difficult to handle, since it doesn’t work like any other Linux system. I.e. the installation to hard drive is very special, the file system is different and NixOS uses special commands, which you can’t use in any other Linux system. However, if you follow my instruction below you can install NixOS without messing up your current Grub boot configuration and finally enjoy NixOS running from hard drive.
INSTRUCTION
1. Download NixOS and install the ISO to a USB stick using Rufus 3.10 in Windows. Start up your computer from the USB stick
2. Install NixOS by following the NixOS Installation Manual
3. Add the lines below to /etc/nixos/configuration.nix and be sure not to install Grub during the NixOS installation. Open configuration.nix with Nano.
boot.loader = {
grub.enable = true;
grub.version = 2;
grub.device = “nodev”;
};
4. Reboot and start up the Linux system (for example Ubuntu) where you have Grub installed. Add the lines below to /boot/grub.cfg or
/etc/grub.d/40_custom
menuentry ‘NixOS’ {
boot.loader.grub.device = “nodev”;
set root='(hd0,X)’
configfile ‘/boot/grub/grub.cfg’;
}
NOTE1: You shall of course replace “X” with the correct number for your install partition. For example (hd0,6)
5. If something goes wrong you can always chroot (change root) into your NixOS partition. Do it like this.
A) Start up your computer from the NixOS DVD or USB stick and run the command mount /dev/disk/by-label/nixos /mnt
B) Then run the command nixos-enter
C) You can also do a manual chroot from any Linux system – watch this screenshot
D) Now you can install any extra (or missed) packages. Example: nix-env -i wireless-tools
NOTE2: When installing packages in chroot you may get an error message saying that the “Operation is not permitted”.
That can be fixed by adding the line nix.readOnlyStore = false to the end of /etc/nixos/configuration.nix.
NOTE3: While in chroot you may not get a Internet connection. That is fixed by editing /etc/resolv.conf. Add the line nameserver 8. 8.8.8. Open resolv.conf with the command nano /etc/resolv.conf.
Difficulties with NetworkManager
If you can’t get a Internet connection through WiFi when you have started NixOS from hard drive you should start up your computer from the DVD/USB stick again and chroot as described above.
A) Then install NetworkManager and NM-applet with the command: nix-env -i network-manager network-manager-applet
B) Edit /etc/nixos/configuration.nix like this – see below. (Open the file with Nano).
networking.wireless.enable = false;
## Only one daemon, wireless or networkmanager, could be ## enabled at the same time.
networking.networkmanager.enable = true;
C) Rebuild NixOS with the command:
nixos-rebuild switch –upgrade –show-trace
D) Reboot and start NetworkManager service daemon with the command: systemctl restart networkmanager
NOTE: The last command may not be necessary. If you see the NM-applet to the right in the panel just click on it and connect.
About multiboot with Grub
On the computer where I now have NixOS installed I also have nine (9) other Linux systems and Windows 10 installed. Study my Grub configuration (/boot/grub/grub.cfg). You may also find my instruction How To dual boot, triple boot or multi boot Linux with Windows in a simple way and be happy interesting.
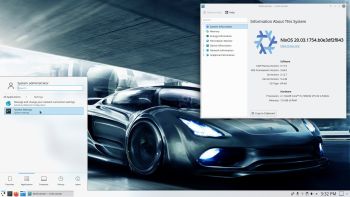
Screenshots from my NixOS installation
1. The Desktop when running as root
2. The Desktop when running as an ordinary user
3. Spotify is running (install Spotify with the command: nix-env -i spotify)
Good luck! /exton

Read about my Android-x86 Systems – 10, Pie, Oreo, Nougat, Marshmallow, Lollipop and KitKat at
andex.exton.net – latest is AndEX 10 (with GAPPS) and AndEX Pie 9.0 (also with GAPPS)!
and
about my Pie, Oreo, Nougat, Marshmallow and Lollipop versions for Raspberry Pi 3/2 at
raspex.exton.se – latest is RaspAnd Pie 9.0 (without GAPPS) and RaspAnd Oreo 8.1 (with GAPPS)!
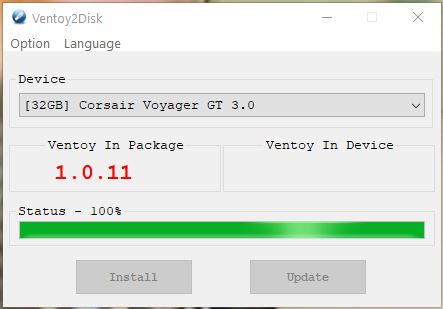
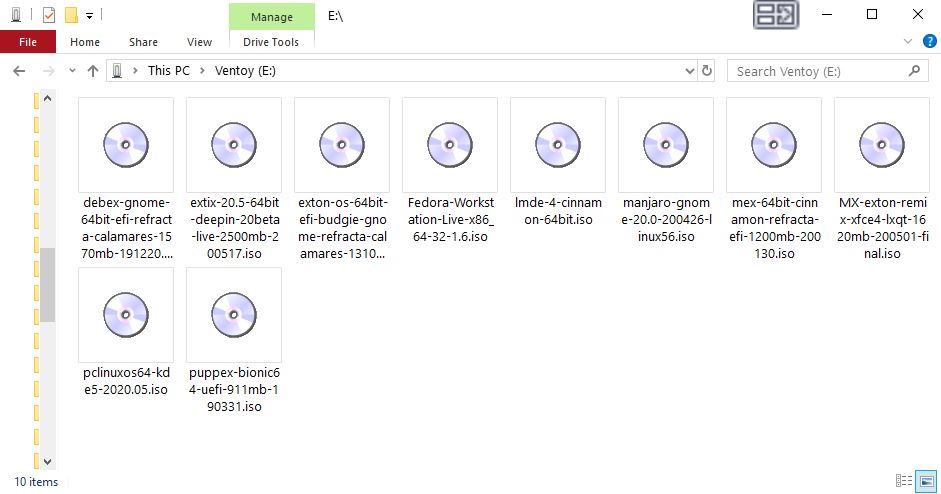
 Ventoy 1.0.11 with persistence support was released yesterday (200523). I’ve tested Ventoy today.
Ventoy 1.0.11 with persistence support was released yesterday (200523). I’ve tested Ventoy today.